Autonomous, Ultra-low Power Receiver Design
Introduction
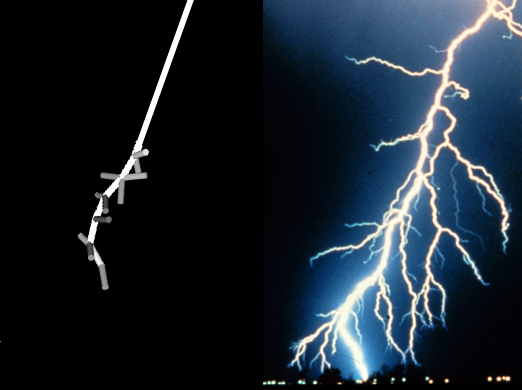
ELF/VLF radio signals, in approximately the 300Hz to 30kHz band, are commonly used for ionospheric remote sensing, geophysical prospecting, and studies of the near-Earth space environment. Naturally occurring ELF/VLF emissions from lightning strikes can be detected for thousands of miles and provide an abundance of wave-particle interaction possibilities in the radiation belts.